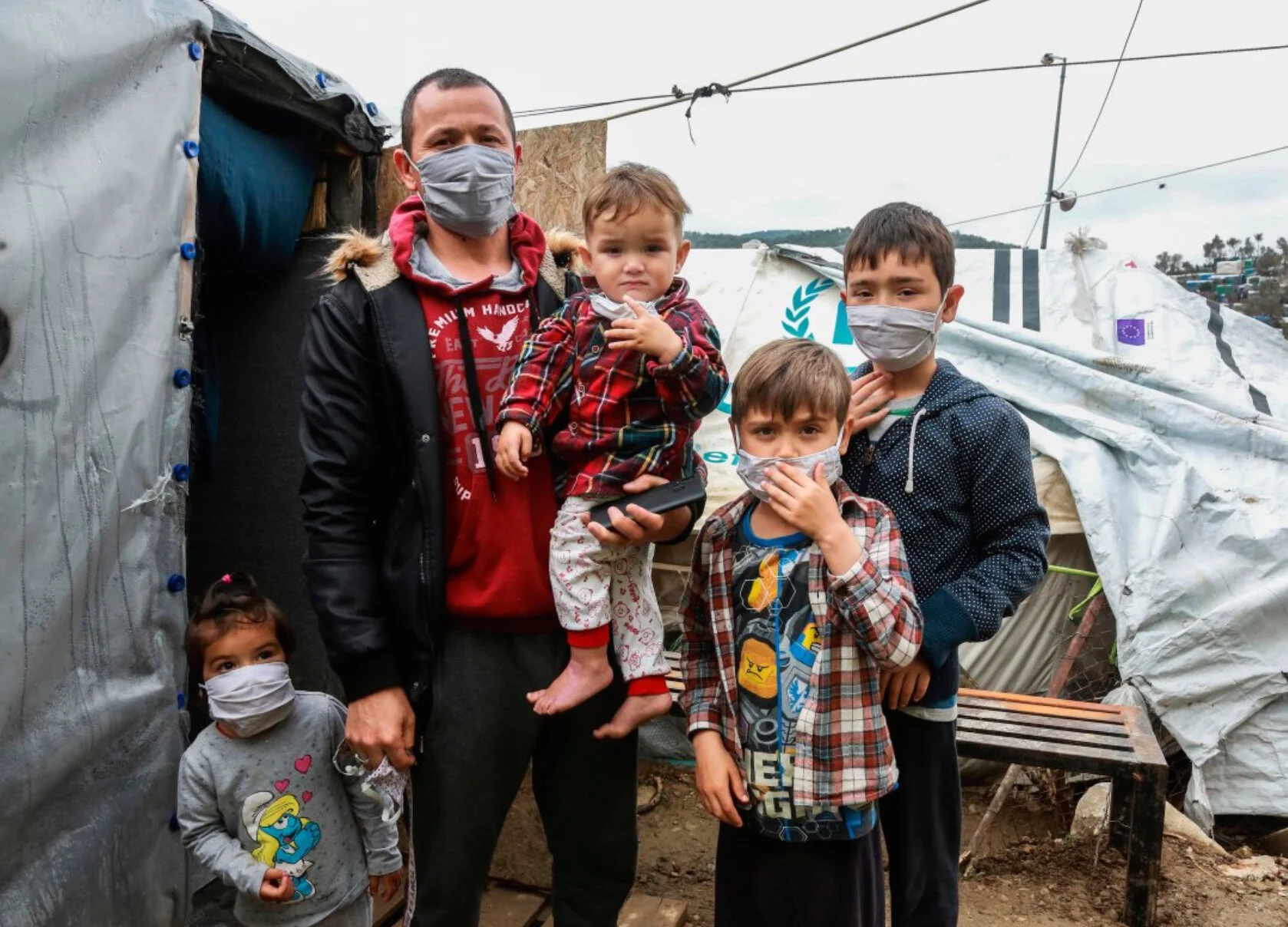
Trump, who campaigned on an anti-immigrant message, targeted the refugee program as soon as he took office, almost immediately slashing admissions from 110,000 to 50,000 and pushing the cap down further each year, ending with a ceiling of 15,000 for the current fiscal year.
It was an enormous deviation for the program, which has been robustly supported by both Republican and Democratic presidents and held up as an example of American's moral leadership. The annual ceiling on admissions has historically averaged about 95,000.
Resettlement in the U.S. involves a complex web of private and public partners. It is largely handled by nine major nongovernmental organizations that work with the State Department and either have local offices around the country or partner with local agencies. The federal government, which vets and processes refugees before they are allowed into the country, gives the agencies funding based on how many refugees they settle. Most states also contribute funding, and agencies also rely on volunteers and donations.
Pushing admissions to record lows, therefore, has had a domino effect: Significantly fewer admissions means significantly less money. Less money means fewer staff and fewer offices. "If you wanted to kill a refugee program, this was the way to do it. You squeeze it to death, you strangle it slowly," Moeller says.
The loss of expertise and intellectual capital will be difficult to restore, experts say. Moeller notes that refugee resettlement is an economy of scale: The larger number of refugees an agency serves allows it to be more efficient with staffing and services. Significantly lower admissions also affect whole ecosystems of services that have been grown and nurtured over the years to support newly settled refugees, says Hans Van de Weerd, interim senior vice president, Europe, at the International Rescue Committee, one of the nine major resettlement agencies. "A lot of the systems that benefit from the regular flow of refugees and immigrants arriving get really, really damaged," Van de Weer says of lowered admissions.
Employers that partner with resettlement agencies to provide opportunities for refugees, for example, needed to find other streams of workers when refugee admissions dried up, Van de Weerd says. Losing those partnerships will have a lasting impact, even as admissions ramp back up under Biden.
"The infrastructure and capacity is not there," Moeller says. "The sinews have not been maintained to ensure that the partnerships we need to be effective are knit together."
It wasn't just the raw admissions numbers. The Trump administration also imposed additional bureaucratic barriers on refugees while shuttering refugee offices and reassigning refugee officers.